What are 5G Private Networks ?
🌐 Introduction
In the dawn of the digital age, the world is rapidly embracing the fifth generation of wireless technology, commonly known as 5G. While the general population is excited about faster internet speeds on their smartphones ([[5G MBB]]), the business sector is buzzing about 5G private networks.
These are not just faster versions of previous networks but the beginning of a transformative era for industrial connectivity. Let’s dive in to understand the essence and rising global influence of these networks.
📡 Understanding 5G Private Networks
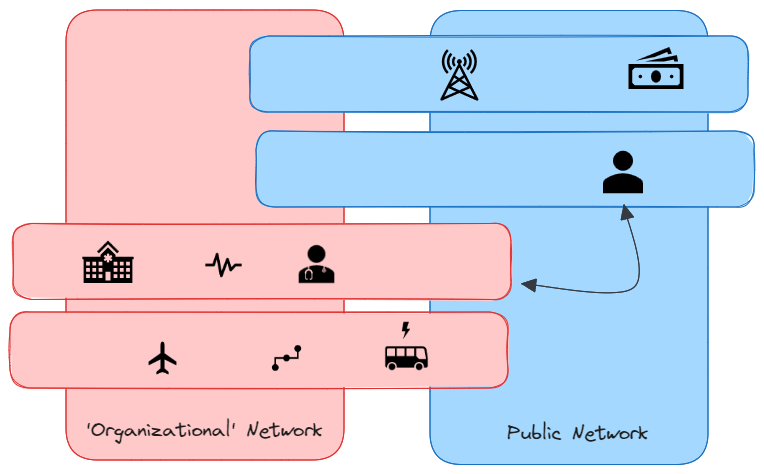
5G private networks are customized platforms, exclusively crafted for specific entities, organizations or functionalities. They stand apart from public networks in significant ways:
🏗 Dedicated Infrastructure:
- Owns its infrastructure, ensuring tailored service quality.
- Provides unparalleled security and data management.
📍Localized Deployment:
- Often tailored for specific regions, like factories or campuses.
- Offers high reliability and minimal latency, catering to tailored needs.
🛡 Superior Security:
- Restricts external access, ensuring a safer digital environment.
- Reduces vulnerabilities, bolstering data protection.
🏭 Industrial Imperatives for 5G Private Networks
⚡ Reliability and Latency:
- Critical ops, like factory robotics, demand instant responses.
- Promises minimal latency and steadfast reliability.
💽 Data Management:
- Industries like finance benefit from enhanced security.
- Ensures better regulatory compliance, especially for sensitive data.
🧩 Customization:
- Tailored to specific bandwidth ([[more on that]]) or protocol requirements.
- Adaptable to varied industrial needs.
🌍 Global Adoption of 5G Private Networks
Various sectors harness the adaptable nature of 5G private networks. Each domain finds unique applications, realizing potential benefit From healthcare to entertainment, sectors are integrating 5G private networks: often termed as ‘governmental networks’.
🏭 Manufacturing:
- Real-time monitoring of machinery and processes to ensure maximum efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance to foresee potential malfunctions and proactively address them.
- Enhanced connectivity ensures seamless communication between different sections of a manufacturing unit, from inventory to the assembly line.
🩺 Healthcare:
- Improved telemedicine capabilities, allowing doctors to virtually diagnose and treat patients from anywhere.
- Robotic surgeries where high-speed, reliable connection is a matter of life and death.
- Real-time patient monitoring, ensuring immediate medical response to emergencies.
🚄 Transportation and Logistics:
- Ports and logistics hubs utilize 5G private networks for real-time cargo tracking and efficient resource allocation.
- Airports leveraging 5G for better crowd management, security surveillance, and automated check-ins.
- Railways and public transit benefit from instantaneous communication, optimizing scheduling and reducing downtime.
🎮 Entertainment:
- Event organizers are harnessing the speed and reliability of 5G for live streaming concerts and events.
- Seamless AR/VR experiences without lags or interruptions, providing attendees with immersive experiences.
- High-definition content streaming ensures the audience gets the best visual and auditory experience.
🔄 The Distinction: Public vs. Private 5G Networks
To grasp the allure of private networks, it’s crucial to differentiate them from public counterparts based on:
- Access: Public networks cater to the masses, while private ones restrict access.
- Isolation: No performance degradation due to dedicated resources.
- Security: Heightened control ensures superior security.
☁️ Cloud-Native Infrastructure: Hurdles & Horizons
Migrating to cloud-native infrastructure for these networks offers:
- Challenges: Data security and multi-cloud deployments.
- Opportunities: Enhanced scalability and resilient infrastructure.
💡 Augmenting with Edge Computing & AI
Marrying AI and edge computing can supercharge 5G private networks:
- Performance: Reduced latency through localized data processing.
- Reliability: Predictive algorithms optimize the network.
- Innovation: AI fosters automation and intelligent responses.
🤝 The Path Forward: Openness & Collaboration
Unleashing the full prowess of these networks demands:
- Openness: Embrace open-source solutions.
- Agile Culture: Foster adaptability and continuous learning.
- Partnerships: Co-create solutions with tech partners.
📶 LTE vs. 5G: The Continuing Relevance of LTE
While 5G has become the talk of the town, it’s crucial to note that LTE’s relevance hasn’t waned as some . Here’s why:
📅 Maturity:
- LTE has been around, ensuring time-tested stability and trustworthiness.
- Its seasoned status translates to a robust network with proven solutions to various challenges.
💰 Economic Feasibility:
- Upgrading to 5G requires substantial infrastructural investment.
- For many businesses, especially in developing regions, LTE remains a cost-effective solution.
🌍 Coverage:
- LTE has widespread coverage, including in regions where 5G hasn’t penetrated yet.
- In remote or less developed areas, LTE might be the primary wireless communication standard.
🛠 Established Devices and Infrastructure:
- Many devices in circulation are LTE-compatible but not necessarily 5G-ready.
- Infrastructure such as towers, base stations, and backhaul for LTE is already in place, minimizing further capital expenses.
🔄 Backward Compatibility:
- Older devices that can’t support 5G can still work efficiently on LTE networks.
- LTE can serve as a fallback network, ensuring continuous connectivity when 5G signals are weak or unavailable.
🚀 Continuous Evolutions of LTE:
- As technology advances, iterations like LTE-Advanced and LTE-Advanced Pro have emerged, offering faster speeds and better performance, closing the gap with early 5G networks.
- Such iterations extend the life and relevance of LTE, ensuring that it remains a viable option for many users and industries.
📑 Summary:
while 5G offers advanced features and capabilities, LTE is still a viable choice for many organizations based on their specific needs, budgetary constraints, and strategic considerations. As with any technological decision, it’s all about picking the right tool for the job.
🌐 Conclusion
5G private networks are steering a novel chapter in industrial digital connectivity, marking milestones in efficiency, security, and innovation. Their current implementation is significant, the horizon promises even more expansive integration.
As we look to the future, the collaborative interplay of technology, strategy, and open innovation will determine the success trajectory of these networks.
comments powered by Disqus
